A large tern, as the name anticipates, the legs are black at all ages and relatively short. The body is white, with a light, chalk-coloured upperpart. The head has a black hood running from the upper base of the bill, under the eyes and down to the nape. The head feathers form a characteristic and very striking plume, especially in the mating season, which gives it the appearance of an elongated head. The back, which is also black, is tipped with a yellow spot.
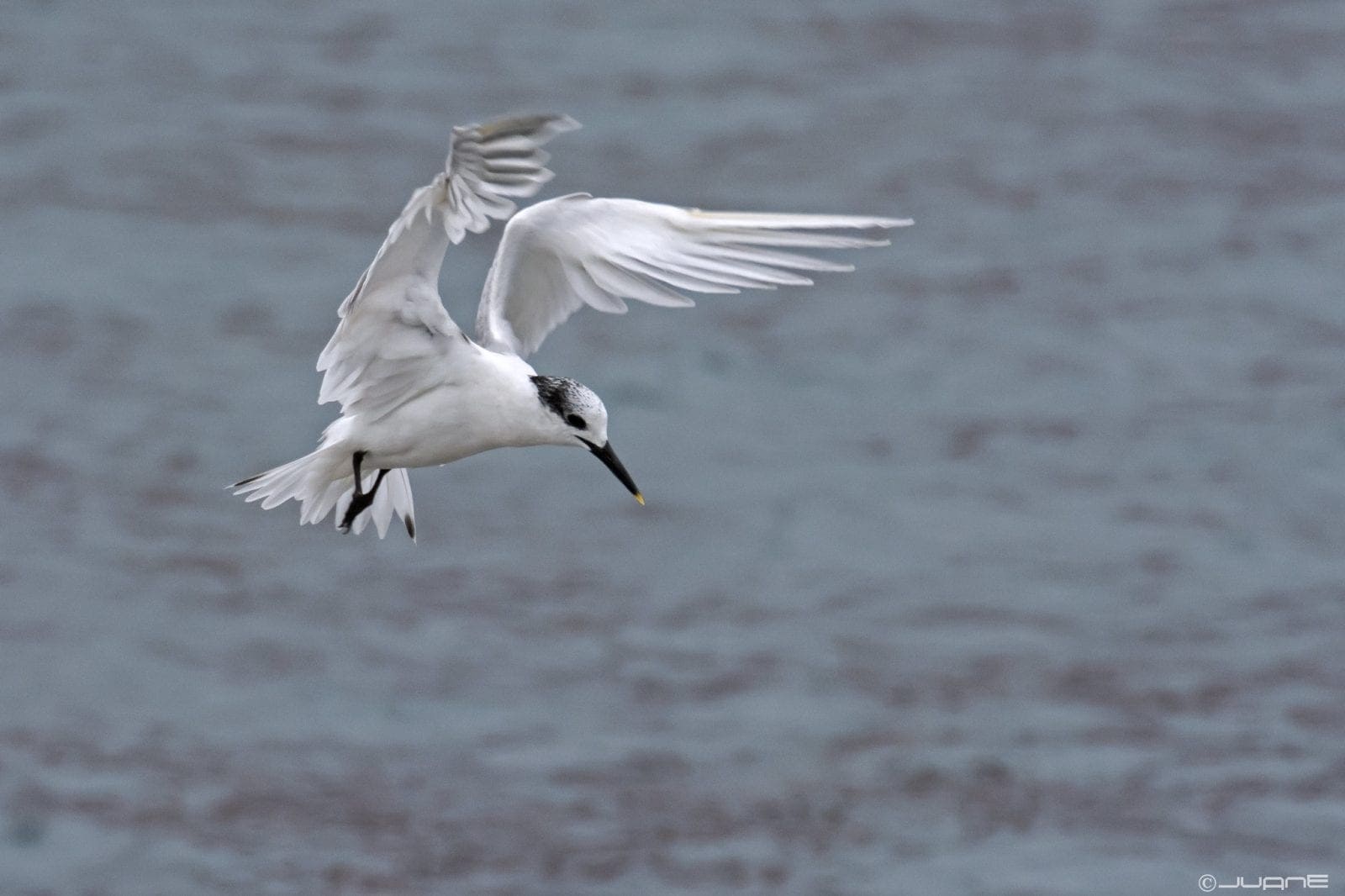

La imagen es autoría de Juan Emilio. Licencia Creative Commons con algunos derechos reservados.
Species 1
Sandwich Tern
Scientific name
Family 2
Taxonomic Affinity Group 3
Phenology 4
It is a resident bird on the Iberian Peninsula, although in Roquetas de Mar it can be seen in summer, especially during the post-nuptial migratory passage, when most of the sightings are concentrated
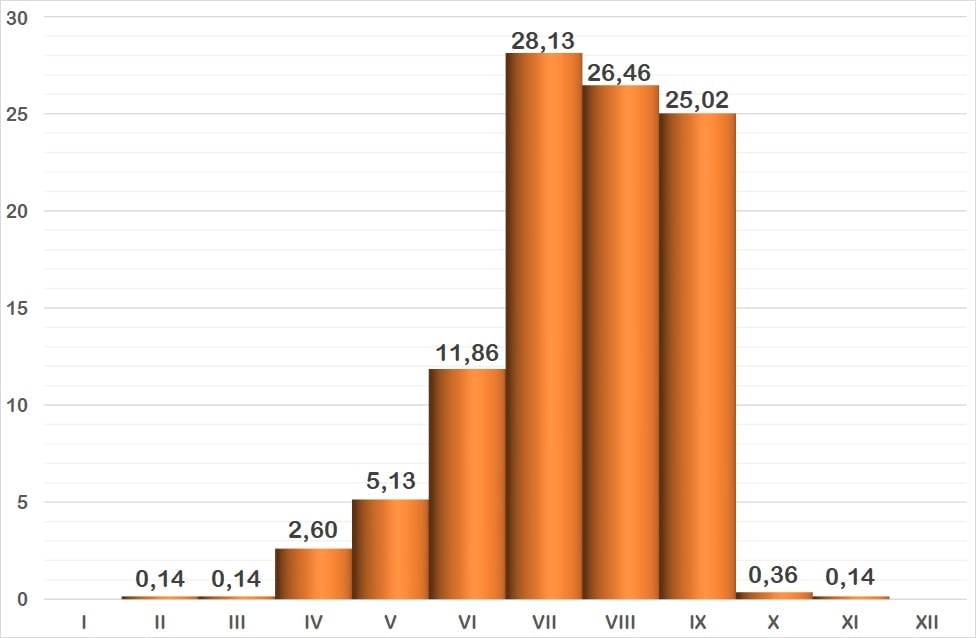
The graph represents the probability of seeing a species during the year, grouped into months. The vertical axis indicates the percentage value. Each of the bars expresses its value. The horizontal axis represents the months: I = January, II = February, III = March, IV = April, V = May, VI = June, VII = July, VIII = August, IX = September, X = October, XI = November and XII = December.
Observation recommendations
It is easy to spot it perched after feeding, and it is also easy to observe it feeding, especially along the coast, where its dives are more striking than those of Little Terns due to their size.
Observation areas where we can find it
Notes
[1] The names used are from the list of birds of Spain, drawn up by SEO/BirdLife and updated to 2019 (https://seo.org/listaavesdeespana/). The reference is: Rouco, M., Copete, J. L., De Juana, E., Gil-Velasco, M., Lorenzo, J. A., Martín, M., Milá, B., Molina, B. & Santos, D. M. 2019. Checklist of the birds of Spain. 2019 edition. SEO/BirdLife. Madrid.
[2] The taxonomic family to which it belongs is indicated.
[3] Traditionally, waterbirds have been grouped according to their taxonomy or “taxonomic affinity”, i.e., when some birds coincide in certain features that allow them to be classified scientifically, but without leaving the rigour of science, they are put together in these groups so that they can be easily recognised. These groups are the following: Greves (belonging to the Podicipedae family), Herons and Similar (includes the families: Ardeidae -Herons- Ciconiidae -Storks- and Threskiornithidae -Ibises and spoonbills-), Ducks (the whole Anatidae family), Coots and Similar (the family Rallidae corresponding to Rails, Gallinules and Coots), Cranes (also with only one family, the Gruidae), Waders , a heterogeneous group, the most diverse of this classification, includes the families Burhinidae (Stone-curlews), Haematopodidae (Oystercather), Recurvirostridade (Avocets and Stilts), Glareolidae (Pranticole), Charadriidadea (Plovers), Scolapacidae and finally Gulls and Similar (the recently unified family Laridae, i.e. Gulls and Terns).
[4] Phenology studies the relationship between the cycles of living beings and meteorological factors, and in our latitude these factors manifest themselves as variations throughout the year, thus relating the seasons to the birds’ cycles (breeding, migratory journeys, etc.) The graph shows the probability of seeing a bird depending on the month. It uses data from 48 bird censuses carried out between October 2016 and September 2018. The method used is that of a census route with sampling stations, with a total count on the sheet of water.
